Capture Electric Power from the Sun with Solar Photovoltaic
 In 1954, Bell Laboratories introduced the first version of a modern Solar Photovoltaic (PV) cell. The company saw this invention as the new way to supply power to rural phone lines. But as it turns out, this technology had a much broader application as well.
In 1954, Bell Laboratories introduced the first version of a modern Solar Photovoltaic (PV) cell. The company saw this invention as the new way to supply power to rural phone lines. But as it turns out, this technology had a much broader application as well.
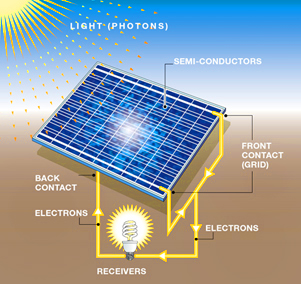
A Solar PV cell works to directly convert the sunlight into electric power. These PV cells are most commonly created with a material made from silicon that operates by reacting to the light produced by the sun. This is different from Solar Thermal panels that use the warmth from the sun to produce heated water for the home. Within the PV cells, semiconductors change the sunlight into electricity. This process starts when the photons in the sun hit the silicon layer on the cell which then offsets the electrons in the semiconductor. This reaction continues which creates a constant stream of electrons, thereby creating the electric current. To increase the electric current, lots of small solar cells are put together to create a solar module (solar panel). Multiple panels then create a solar array which combines the power to collectively send all of the energy to the inverter.
Watch our video on about the Solar PV panels on the roof of our Highland, WI store.
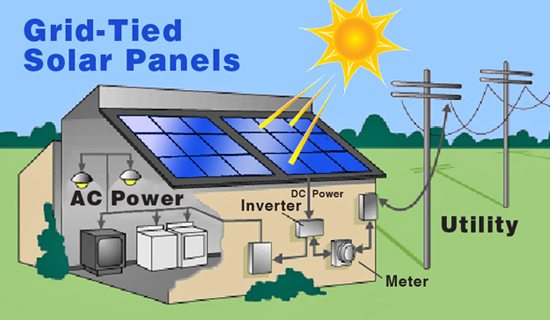
Solar PV can be linked directly in with the power grid to feed excess electricity back into the grid and more electricity out when necessary.
The energy from the solar panels comes in as direct current (DC) power. Therefore, the electric energy must be switched over to alternating current (AC) so that it can be used to provide electricity for the building. This way the power can also be linked to the electric meter and into the power grid. Now the power that you do not consume yourself can be sold to the utility company and when you need more power than the solar panels produce, you can still receive additional power from the power company. This connection to the grid will also shut down the transfer of electricity when the power shuts off to protect the power workers during the outage. But a simple battery operated inverter will allow the solar power to be used at this time without a connection to the grid. This switch will be made in a fraction of a second to allow the solar electricity to supply the critical load sub-panel with power, so you will have power during an outage, when no one else around you does.
 Currently, two main types of silicon based solar panels exist. They both differ sightly in their price, effectiveness and life span. The panel that is most effective at changing the sunlight into power is called the Monocrystaline variety. This type of solar panel will work for over 25 years and coverts the energy at the highest rate, about 18 percent. But this type of panel is also the most expensive. Next is the Polycrystaline type that has a similar conversion rate of about 15 percent. These panels last about the same amount of time as the Monocrystaline but are slightly less expensive. The Polycrystaline solar panels are currently the most common Solar PV type of panels.
Currently, two main types of silicon based solar panels exist. They both differ sightly in their price, effectiveness and life span. The panel that is most effective at changing the sunlight into power is called the Monocrystaline variety. This type of solar panel will work for over 25 years and coverts the energy at the highest rate, about 18 percent. But this type of panel is also the most expensive. Next is the Polycrystaline type that has a similar conversion rate of about 15 percent. These panels last about the same amount of time as the Monocrystaline but are slightly less expensive. The Polycrystaline solar panels are currently the most common Solar PV type of panels.
Besides these two main types of panels, there is a variety called thin film Solar PV cells containing Amorphous Silicon or Cadmium Telluride. These cells can be mass produced at a relatively low cost but they do not last as long as the others and they do not convert as much electricity. They are easier to make so they are often used in large scale projects, but the material Cadmium is toxic, so there are some environmental concerns with using this variety of the solar cells.
With these thin Solar PV cells scientists have been able to get creative with the various applications for how these cells are used. Because of the small size, these cells can be used to cover a large variety of materials to generate electric power including roofing materials and other household fixtures. Solar PV has come a long way since its 1954 beginnings and will only continue to become more prevalent and accessible as time goes on.







